Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths globally. Despite advances in early detection and treatment, the prognosis for individuals diagnosed with stomach cancer can vary significantly. In this article, we’ll explore the factors that influence the stomach cancer survival rate, the stages of gastric cancer, and what patients can expect in terms of life expectancy after diagnosis.
Understanding Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer develops in the lining of the stomach and can spread to nearby organs. It often goes undetected in its early stages due to vague and non-specific symptoms, which can delay treatment. The condition is more common in older adults, with a higher prevalence in men than women. Although it remains a challenging diagnosis, the survival rate for stomach cancer has improved over time thanks to better detection methods, treatment options, and patient care.
The Stomach Cancer Survival Rate: What Does It Really Mean?
Survival rates are statistical measures used by doctors to give an idea of the percentage of people who survive a certain type of cancer for a specific period after diagnosis.
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of stomach cancer is 70%, it means that people who have that cancer are, on average, about 70% as likely as people who don’t have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
For stomach cancer, the survival rate is often measured at five years, though it’s important to note that survival rates can vary greatly depending on several factors, such as the stage of cancer at diagnosis, the patient’s overall health, and the treatment approach.
The Five-Year Survival Rate
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for stomach cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages (stage 1, stage 2, stage 3, etc.). Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the stomach.
- Regional: The cancer has spread outside the stomach to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, such as the liver.
These numbers are based on people diagnosed with cancers of the stomach between 2014 and 2020.
| SEER Stage | 5-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|
| Localized | 75% |
| Regional | 36% |
| Distant | 7% |
| All SEER stages combined | 36% |
The five-year survival rate for stomach cancer has traditionally been low, mainly due to the fact that the disease is often diagnosed in later stages. However, survival rates are improving as awareness, early detection, and treatment options advance.
According to the American Cancer Society, the overall five-year survival rate for stomach cancer is approximately 36%. This means that about 36% of people diagnosed with stomach cancer will live at least five years after diagnosis. However, this figure varies widely based on several factors.
Stage at Diagnosis: A Key Factor
One of the most significant determinants of survival is the stage at which stomach cancer is diagnosed, which is based on the layer of the stomach and the lymph nodes involved. The earlier the stage, the better the prognosis.
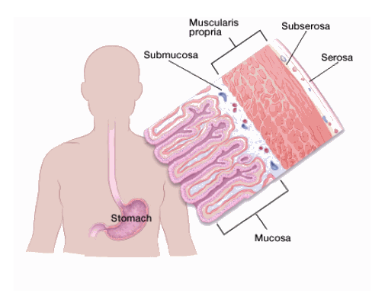
The 5 layers of the stomach wall include:
- Mucosa: the innermost layer, where nearly all stomach cancers start.
- Submucosa: a supporting layer under the mucosa.
- Muscularis propria: a thick layer of muscle that moves and mixes the stomach contents.
- Subserosa.
- Serosa: the outermost wrapping layer of the stomach.
Stage 1
At this early stage, cancer is confined to the inner layers of the stomach (mucosa and/or submucosa). The survival rate can be as high as 80% to 90%, but early detection is crucial.
Stage 2
The cancer extends into the muscularis layer and maybe to nearby lymph nodes or tissues, but it is still contained within the stomach. The five-year survival rate for stage 2 stomach cancer drops to about 50% to 60%.
Stage 3
The cancer penetrates into the subserosal layer without invasion of the peritoneum or adjacent structures. At this stage, the survival rate decreases to around 30%.
Stage 4
In this advanced stage, stomach cancer has spread to distant organs, such as the liver, lungs, or peritoneum. The survival rate for stage 4 stomach cancer is around 5% to 10%.
And while these figures can provide a general sense, it’s important to remember that every patient’s situation is unique. Factors such as age, overall health, and response to treatment can also play a significant role in survival.
What Affects the Stomach Cancer Survival Rate?
Several factors influence the stomach cancer survival rate, including:
1. Early Detection and Diagnosis
As with most cancers, early detection is key to improving survival rates. Regular screening for those at high risk such as individuals with a family history of stomach cancer or a history of gastric conditions can lead to earlier diagnoses and more effective treatments.
2. Treatment Options
Treatment for stomach cancer may involve surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of these.
For patients diagnosed in the early stages, surgery to remove the tumor may offer the best chance for a cure. In more advanced stages, chemotherapy and radiation therapy can help reduce the tumor size and manage symptoms, potentially improving survival.
3. Age and Overall Health
Older adults may face more challenges when dealing with stomach cancer, especially if they have other underlying health conditions. A person’s overall health, including their ability to tolerate treatments like chemotherapy, plays a significant role in determining outcomes.
4. Genetic and Lifestyle Factors
Certain genetic factors, such as mutations in the CDH1 gene, have been linked to an increased risk of developing stomach cancer. Lifestyle factors, such as diet, smoking, and alcohol consumption, can also impact survival rates.
A diet rich in smoked or salted foods has been associated with a higher risk of stomach cancer, while maintaining a healthy diet can help improve prognosis.
The Role of Surgery in Gastric Cancer Survival
Surgery is often the most effective treatment for early-stage stomach cancer, offering the possibility of a cure. The type of surgery depends on the location and extent of the cancer. Common procedures include:
- Partial gastrectomy: Removal of part of the stomach.
- Total gastrectomy: Removal of the entire stomach, often followed by the creation of a new pathway for food to travel through the digestive system.
While surgery is crucial for many patients, it’s often combined with chemotherapy or radiation to target remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Managing Stomach Cancer: What Can Patients Expect?
The prognosis for stomach cancer patients depends not only on the cancer stage but also on how well they respond to treatment. Survivors of stomach cancer often face long-term challenges, including changes in digestion, nutritional deficiencies, and potential recurrence of the cancer. Survivors may also experience emotional and psychological effects, such as anxiety or depression, which can impact their overall well-being.
International Patients Seeking Treatment: Travel for Stomach Cancer Care
In some cases, patients may seek treatment for stomach cancer outside their home country. This may be due to better treatment options, advanced medical technologies, or even lower costs in some regions.
Countries like India, South Korea, and Thailand have become popular destinations for international patients due to their high-quality medical care and skilled surgeons.
While traveling abroad for cancer treatment can offer patients access to cutting-edge care, it also requires careful planning. Patients need to consider factors such as visa requirements, medical tourism packages, travel and accommodation arrangements, and the ability to follow up on treatment once they return home.
Prognosis and Life Expectancy: Looking Ahead
The life expectancy for individuals with stomach cancer varies greatly. As previously mentioned, those diagnosed in the early stages have a much better chance of survival. But even for patients diagnosed at later stages, advances in treatment such as targeted therapies and immunotherapy offer new hope.
While the overall stomach cancer survival rate is still relatively low, ongoing research into the disease’s causes, early detection methods, and treatment options is paving the way for better outcomes in the future. For many patients, the key is not to lose hope and to seek the best treatment options available.
Conclusion
The stomach cancer survival rate is influenced by numerous factors, including the stage at diagnosis, treatment options, and individual health conditions. With early detection, advanced treatments, and a holistic approach to care, many patients can live longer and fuller lives after a diagnosis of gastric cancer.
Though the journey may be difficult, ongoing research and improved medical practices continue to enhance the prognosis for those affected by this challenging disease. By understanding the factors that impact survival and seeking the right treatment, patients can significantly improve their chances of overcoming this deadly disease.